Photo Essay
Vetiver Grass - Vetiveria zizanioides
Part 3 --- Planting Material
Parts 1 and 2 described the plant and how it can be used to create hedgerows. Part 3
shows how to produce the planting material required to create the hedgerows. Since nearly
all cultivars of Vetiveria zizanoides are either non flowering or virtually
sterile, plant material is produced vegetatively, either as bare roots or in containers.
Both require extensive nurseries, where possible at a site that can provide some
supplementary irrigation. The prime objective in nursery management is to produce the
maximum number of high quality plants per unit area. For nurseries that produce bare
rooted plants three "planting splits" should be planted at each planting station
(30cmx30cm).


The left hand photos shows young planting slips from Vietnam. On the right planting
material comprising three slips per planting plug is being prepared in Zimbabwe. Note most
of the root is cut off (leaving about 7cm), and the leaves are cut to about 12 cm.



Nurseries should be located on good quality soils. Liberal quantities of manure or compost
should be added to assure optimum growth. A good nursery should produce over 1 million
planting plugs per annum. Enough to plant 200 km. of hedgerow. The nursery in the center
is one in Ethiopia. Note the plants are trimmed to about 30 cm to promote tillering. That
on the left is near Sacramento in California. This plant material has not been trimmed,
and the quality of plants will be lower than those in the center. On the right is an
experiment in Thailand where nursery plants were grown in polythene lined trenches. When
ready to dig all that was needed was to pull up the polethene sheet. Note this is not a
common practice.


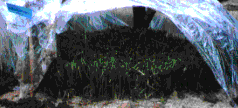
These three photos show on the top left -- the production of planting material grown in
containerised polybags (10 cm diameter); on the top right storing under a poly tent (to
maintain humidity) after removal from the nursery and prior to field planting; and on the
bottom photo containersied plants ready for loading on to a truck.
Generally containerised plants are used to protect high cost works such as highway
embankments etc. Also they are used where stabilization will be difficult (often due to
seasonal high velocity water flows) i.e. stream banks, gullies, etc. and where quick
establishment is required. In all other cases bare rooted plants are lower cost and easier
to handle.
return to photo esseys







